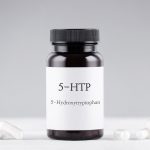
The supplement known as 5-HTP is available in both natural and synthetic versions and is used by some people to treat a variety of wellness issues. Here’s a look at what this supplement is, its safety profile, side effects and drug interactions, and the potential health benefits that 5-HTP has to offer you for a balanced lifestyle. What is 5-HTP? In your body, 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) is a chemical produced naturally from the essential amino acid called tryptophan. The U.S. National Library of Medicine states that it’s the forerunner of serotonin. Natural supplements that contain 5-HTP are made from a plant called Griffonia simplicifolia that’s native to countries in West Africa such as Congo, Sierra Leone and Ghana, according to the University of Texas El Paso. A review published in the International Journal of Molecular Science by researchers from the University of Turin in Italy found that in recent years, scientific breakthroughs have also allowed for the production of some synthetic 5-HTP supplements. 5-HTP benefits Because 5-HTP is converted into serotonin (also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) in the body, it provides a number of potential benefits for your overall health and well-being. Depression The Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database rates 5-HTP as “possibly effective” for treating depression, according to the National Library of Medicine, and it may work as well as some antidepressant drugs that are… read on > read on >



























-300x200.jpg)










